Understanding Hernia
Hernias often manifest as noticeable bulges in areas such as the groin, belly button, or surgical sites and may be accompanied by sharp pain or a dull ache. They can be present from birth (congenital) or develop over time, affecting both men and women.
Hernia Causes
A hernia can be triggered by anything that elevates pressure in the abdomen, encompassing various factors such as:
- Lifting heavy objects without supporting abdominal muscles can lead to hernia development.
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Continuous coughing or sneezing.
- Obesity, inadequate nutrition, and smoking weak muscles increase the chances of hernia.
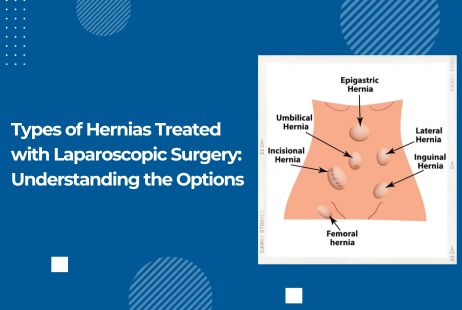
Types of Hernias
The most common types of Hernia are:
Inguinal or groin hernia:
The most prevalent type of hernia, known as inguinal or groin hernia, predominantly affects men (70%) compared to women. This occurs when a segment of the intestine or fatty tissue and a portion of the lining of the abdominal cavity (peritoneum) protrudes through the inguinal canal. This canal serves as the passage through which the testes exit the abdominal cavity and descend into the scrotum during fetal development. The herniation manifests as a bulge in the groin area.
Femoral Hernia:
A femoral hernia occurs when tissue or part of the bowel protrudes into the femoral canal in the inner thigh or groin. While femoral hernias are relatively rare, accounting for a small percentage of cases (a few out of every 100), they are more common in older women and are sometimes misidentified as inguinal hernias. Femoral hernias bulge into the femoral canal, often appearing as a lump around the groin crease or upper thigh.
Umbilical Hernia:
In Umbilical hernia, the part of the bowel protrudes near the navel, common in children, women (especially during pregnancy and obesity), and adults. Risk factors include being overweight, multiple pregnancies, abdominal fluid accumulation, persistent cough, enlarged prostate, constipation, and vomiting. While more common in newborns, they can persist into adulthood.
Incisional Hernia:
An incisional hernia is common in individuals who have undergone prior abdominal surgeries. It occurs when organs or tissues protrude through a partially healed wound from a previous incision or scar. These hernias typically develop at the site of an earlier abdominal surgery incision, where weakened skin allows tissue to poke through.
Hiatal Hernia:
A hiatal hernia linked to acid reflux and symptoms like heartburn occur when part of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragmatic opening, known as the hiatus. This thin muscle separates the chest from the belly, where the esophagus passes through. A hiatal hernia doesn’t result in a visible lump, but individuals may experience heartburn, chest pain, and a sour taste in the mouth. The distinctive feature is the stomach’s herniation into the chest through the diaphragmatic opening.
What are your Treatment Options?
The two main surgical approaches to hernia treatment include:
Open Hernia surgery
In open hernia surgery, a surgeon makes an incision to access the herniated area, then utilizes dissolvable stitches and a synthetic mesh to repair the weakened muscle and prevent recurrence. This procedure involves pushing the displaced organ or fat tissue back into the abdomen.
Anesthesia is administered, and recovery typically takes about 4–5 weeks, during which heavy physical activity is not recommended. The mesh provides additional support, reducing the risk of hernia recurrence, especially in larger hernias.
Keyhole or Laparoscopic surgery
In laparoscopic hernia repair, the surgeon utilizes a minimally invasive approach, viewing the hernia on a screen and guiding the procedure with fine laparoscopic instruments. Under anesthesia, small incisions are made, and a laparoscope is employed for enhanced visibility.
Special tools are inserted to push the hernia back, and a mesh is secured with staples to reinforce the abdominal muscle wall. Incision points are closed with stitches or tape, gradually becoming barely noticeable.
Why should you opt for Laparoscopic Surgery?
Some common reasons include:
- Safe and secure surgical process.
- Minimum invasive.
- Minimizing pain and discomfort post-surgery involves the use of fewer pain medications.
- Short recovery time, about two weeks.
- Quicker return to work and normal activities.
- Fairly a few post-operative complications.
- Excellent cosmetic results due to smaller incisions.
- Detecting and addressing hernias that haven’t become visible allows for earlier identification and repair, reducing the need for additional surgeries later.
Consult Dr. Girish Juneja for your Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery in Dubai
Dr. Girish Juneja, a seasoned surgeon with two decades of experience, has successfully performed numerous advanced hernia surgeries in the UAE for local and international patients. His expertise and the latest techniques ensure top-notch results and patient safety.
Notably, he was the first surgeon in Dubai to receive the prestigious Surgeon of Excellence Award for bariatric surgery from the International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity & Metabolic Disorders in 2017.
Book an appointment now.